Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Dr. Amol Kulkarni

- Aug 9, 2025
- 1 min read
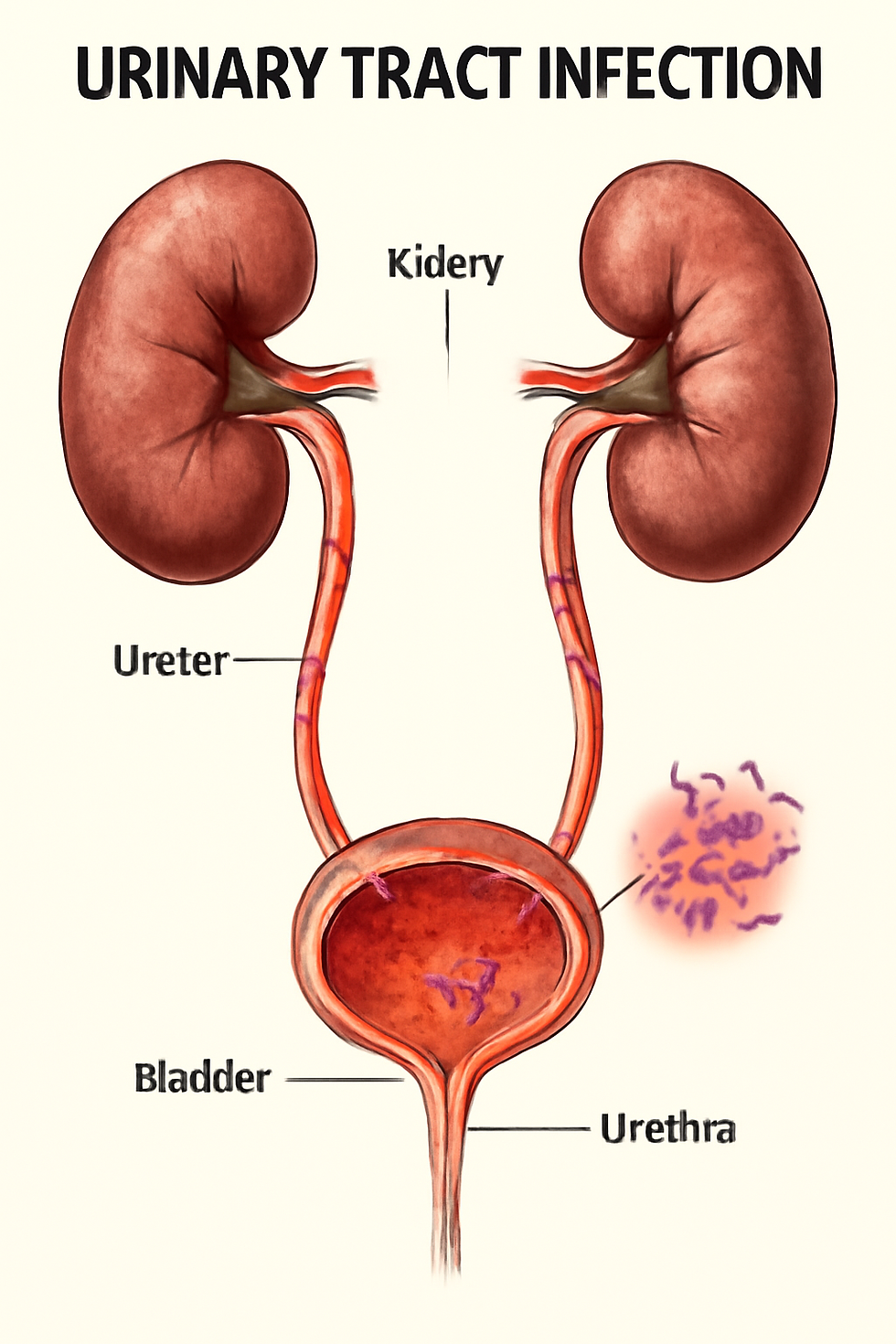
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that can affect any part of your urinary system, including your kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. Most commonly, it involves the lower urinary tract—the bladder and urethra. UTIs are typically caused by bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), which can enter the urinary tract through the urethra and multiply in the bladder. Risk factors for developing a UTI include being female, sexual activity, having urinary tract abnormalities, a suppressed immune system, or using certain types of birth control.
Common symptoms of a UTI include a strong, persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, passing small amounts of urine frequently, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pelvic pain, especially in women. If the infection spreads to the kidneys, you might experience fever, chills, and back pain.
UTIs are generally diagnosed using a urine sample to detect bacteria and white blood cells. Sometimes further tests, such as urine cultures or imaging studies, are needed for recurrent infections. Treatment often involves a course of antibiotics prescribed by your doctor. Drinking plenty of fluids, urinating frequently, and practicing good personal hygiene can also help manage symptoms and prevent future infections. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical care promptly.



Comments