Hypertensive Kidney Disease
- Dr. Amol Kulkarni

- Aug 9, 2025
- 1 min read
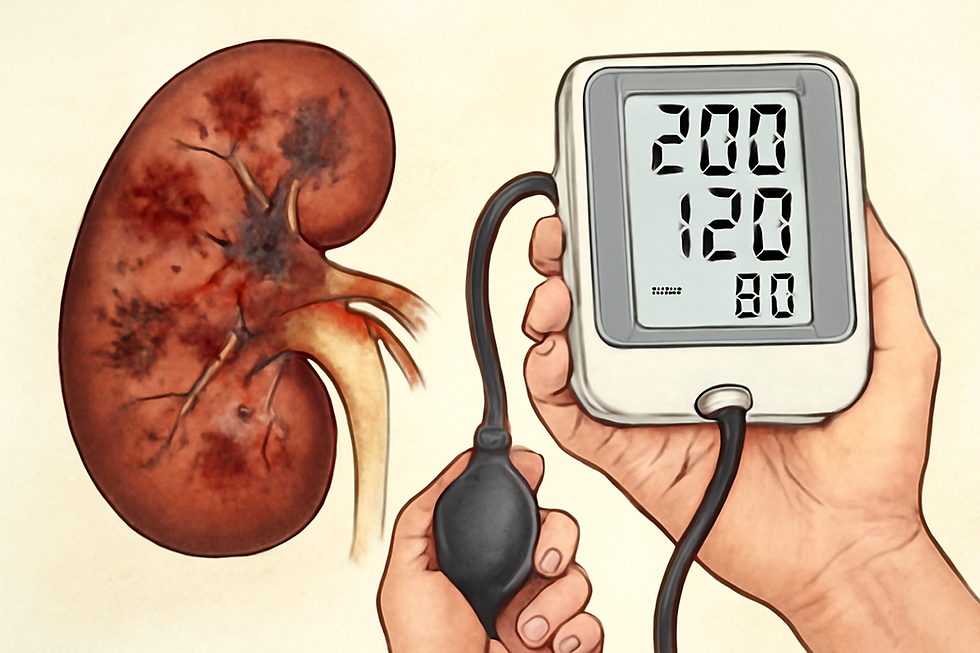
Hypertensive kidney disease is a condition where long-term high blood pressure (hypertension) damages the kidneys. High blood pressure puts extra strain on the blood vessels in the kidneys, making it harder for them to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood. Over time, this can lead to kidney scarring and reduced function.
Causes:The main cause is uncontrolled or poorly managed high blood pressure, especially over many years. Other risk factors include a family history of kidney disease, diabetes, obesity, and smoking.
Symptoms:Early on, hypertensive kidney disease may not cause noticeable symptoms. As the condition worsens, patients might experience swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet, fatigue, nausea, difficulty concentrating, or changes in urination patterns (such as blood in urine or frequent nighttime urination).
Diagnosis:Doctors diagnose hypertensive kidney disease through blood pressure measurements, blood and urine tests to check kidney function, and sometimes imaging tests like ultrasound to assess kidney size and structure.
Treatment Options:The main treatment goal is to control blood pressure to protect kidney function. This may involve a combination of lifestyle changes (like reducing salt intake, exercising, and maintaining a healthy weight) and medications such as ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or diuretics. In advanced cases, dialysis or a kidney transplant may be necessary. Regular doctor visits and strict management can slow disease progression and improve quality of life.



Comments